The Role of Tendonitis in Repetitive Strain Injuries
Understanding Repetitive Strain Injuries
As someone who's been living with a repetitive strain injury, I know first-hand how debilitating it can be. Repetitive strain injury (RSI) is a term for pain and other symptoms resulting from repetitive movement and overuse of certain body parts. The condition mostly affects parts of the upper body, such as the forearms and elbows, wrists and hands, and neck and shoulders.
The symptoms of RSI can range from mild to severe and may persist even after stopping the repetitive activity. They include aching, pulsating pain, stiffness, tingling, numbness, and weakness.
What is Tendonitis?
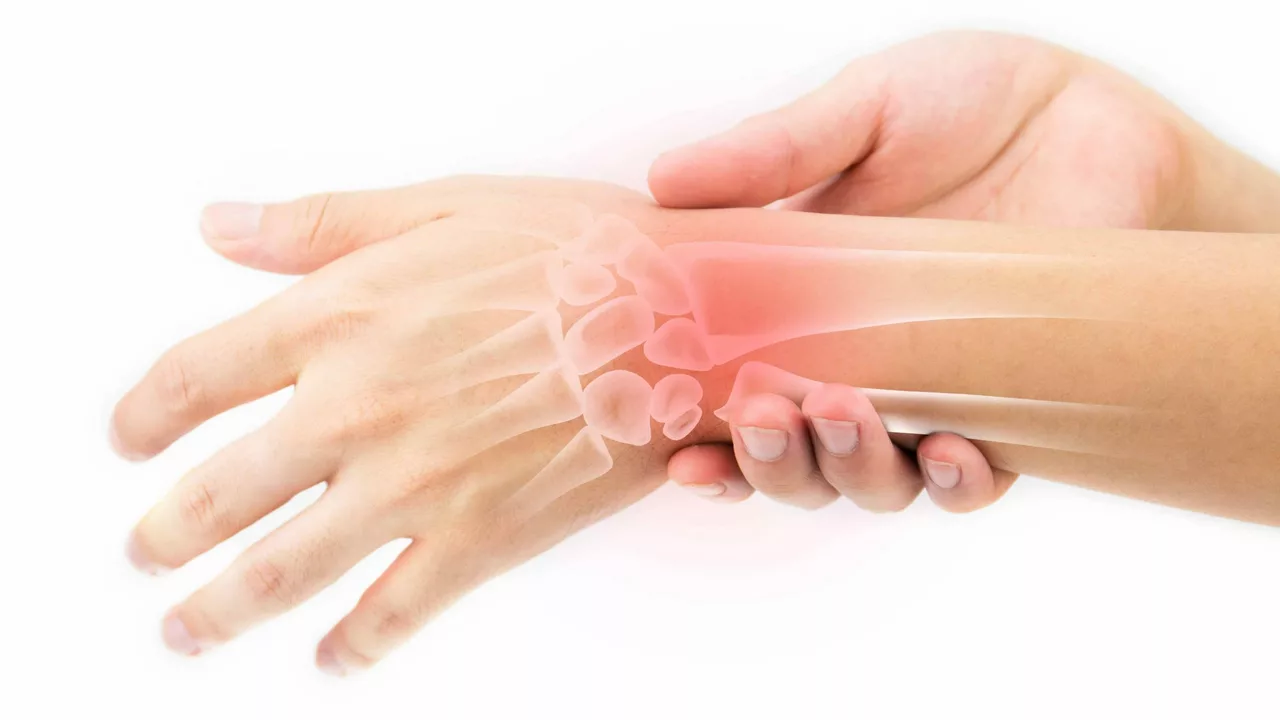
Let's now dive into what tendonitis is. Tendonitis is an inflammation or irritation of a tendon, the thick fibrous cords that attach muscle to bone. The condition causes pain and tenderness just outside a joint. It's most commonly observed in wrists, elbows, shoulders, hips, knees, and ankles. It's often caused by minor, repetitive impact on the affected area, or from a sudden more serious injury.
The Connection Between Tendonitis and Repetitive Strain Injuries
So, how does tendonitis relate to repetitive strain injuries? Well, it's quite simple. Tendonitis is actually one of the most common types of RSI. It's often caused by repetitive tasks, awkward positions, or excessive force. These activities can cause the tendon to become inflamed, which leads to pain, swelling, and impaired function.
Causes of Tendonitis in Repetitive Strain Injuries
Next, let's discuss what causes tendonitis in the context of repetitive strain injuries. Activities that can cause such injuries typically involve repetitive motions or maintaining a certain position for extended periods. For instance, typing on a keyboard, using a mouse, or playing a musical instrument could lead to tendonitis. The risk is amplified if the activity involves forceful exertion, awkward positions, or not taking enough breaks.
Preventing Tendonitis and Other Repetitive Strain Injuries
Prevention is always better than cure, isn't it? To help prevent tendonitis and other repetitive strain injuries, consider taking regular breaks from any repetitive activity, stretching before and after activities, and using appropriate equipment or aids. For example, use an ergonomic keyboard if you type a lot, or wear a wrist brace if you're prone to wrist tendonitis.
Treatment Options for Tendonitis
Let's now talk about treatment options for tendonitis. Generally, the treatment focuses on relieving pain and reducing inflammation. Some options include rest, physical therapy, taking over-the-counter pain relievers, or getting a corticosteroid injection. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary. Always consult with a healthcare professional for the best course of action.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Managing Tendonitis
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing tendonitis. A physical therapist can help improve your strength and flexibility, which can relieve pain and prevent further injuries. They can also show you how to adjust your movements to protect your tendons.
Lifestyle Modifications for Coping with Tendonitis
Finally, let's discuss some lifestyle modifications you can make to cope with tendonitis. Start by maintaining a healthy weight, as excess weight can put more pressure on your tendons. Also, consider stress management techniques like meditation and deep breathing, as stress can cause your muscles to tense up and put more strain on your tendons.
Living with Tendonitis: A Personal Perspective
Living with tendonitis is not easy, but it's certainly manageable. With the right treatment, preventive measures, and lifestyle modifications, you can significantly reduce your symptoms and improve your quality of life. Remember to always seek professional help if your symptoms persist or worsen.

nathaniel stewart
July 12, 2023 AT 11:36Dear fellow readers, I commend your dedication to exploring the intricate relationship between tendonitis and repetitive strain injuries. It is evident that the pursuit of knowledge in this domain is both noble and necessary, especially for those who suffer daily discomfort. While the article presents a comprehensive overview, I would like to emphasize the importance of consistency in ergonomic practices, as even small adjustments can yield remarkable improvements. Moreover, a proactive mindset, combined with patience, often leads to lasting relief and enhanced wellbeing. Do not be discouraged by occasional setbacks; perseverance and optimism are your greatest allies in this journey. Remember, each step forward, no matter how modest, contributes to a healthier musculoskeletal system, and you are undoubtedly capable of achieving it. Stay encouraged, stay informed, and above all, stay hopeful as you navigate your path to recovery.
Pathan Jahidkhan
July 12, 2023 AT 11:38Life repeats like a mantra and tendons whisper their pain in silence. The dance of motion and stillness creates a paradox that fuels inflammation. In the quiet of a night shift the wrist cries, yet the mind persists. Each keystroke becomes a small rebellion against the body’s warning. The drama lies not in the injury itself but in the unspoken pact between habit and health. One must break the cycle, or else be forever bound.
Dustin Hardage
July 12, 2023 AT 11:40It is critical to understand that tendonitis, while often categorized under the broader umbrella of repetitive strain injuries, possesses distinct pathophysiological mechanisms that merit specific attention. Repetitive microtrauma leads to collagen disarray within the tendon matrix, which in turn triggers a cascade of inflammatory mediators. Over time, this process not only compromises tensile strength but also reduces vascular supply, further impeding healing. Consequently, therapeutic strategies must address both the mechanical overload and the biological response. Rest, when appropriately prescribed, allows cellular repair processes to commence without the interference of continued strain. Complementary to rest, graded eccentric loading exercises have been shown in multiple randomized trials to restore tendon elasticity and promote collagen realignment. Physical therapists often incorporate such protocols alongside neuromuscular re‑education to correct faulty movement patterns. Ergonomic interventions, such as keyboard split designs and adjustable workstations, reduce joint deviation and minimize undue force on the tendons. Additionally, the utilization of supportive devices, for instance, wrist splints, can off‑load affected structures during activities of daily living. Pharmacologic measures, including non‑steroidal anti‑inflammatory drugs, may alleviate pain but should be employed judiciously to avoid masking symptoms that guide activity modification. In cases where conservative management fails, ultrasound‑guided corticosteroid injections have demonstrated short‑term efficacy, though the risk of tendon weakening must be weighed. Surgical debridement remains a last‑resort option, reserved for chronic, refractory cases where structural degeneration is evident. Nutritional support, particularly adequate protein intake and anti‑oxidant rich foods, can facilitate tissue repair. Finally, patient education is paramount; individuals must recognize early warning signs and implement timely interventions to prevent progression. By integrating biomechanical, pharmacological, and lifestyle modifications, clinicians can tailor a comprehensive plan that addresses the multifactorial nature of tendonitis within the context of repetitive strain injuries.
Dawson Turcott
July 12, 2023 AT 11:41Wow, look at that epic essay 🙄. Guess we all need a PhD now just to stretch our wrists. Sure, do the "graded eccentric loading" while I stare at my screen. 😂
Alex Jhonson
July 12, 2023 AT 11:43Together we can turn pain into progress.